About the Monorail
Home ⤳ About the Monorail
1961
April 1961
Construction Begins
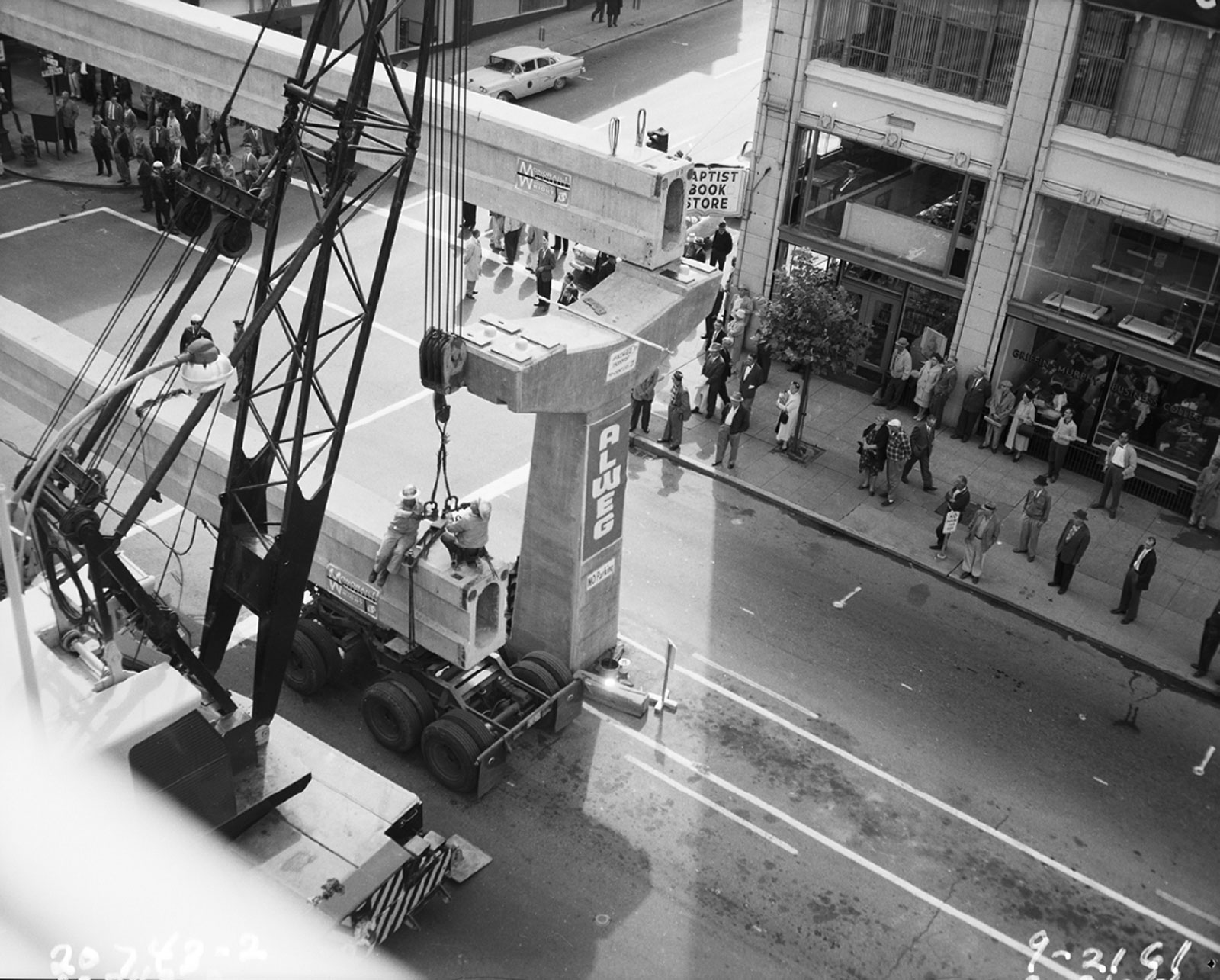
Construction began in April of 1961 by Alweg Rapid Transit Systems, who received the bid when it offered to underwrite the entire cost of construction.

March 1962
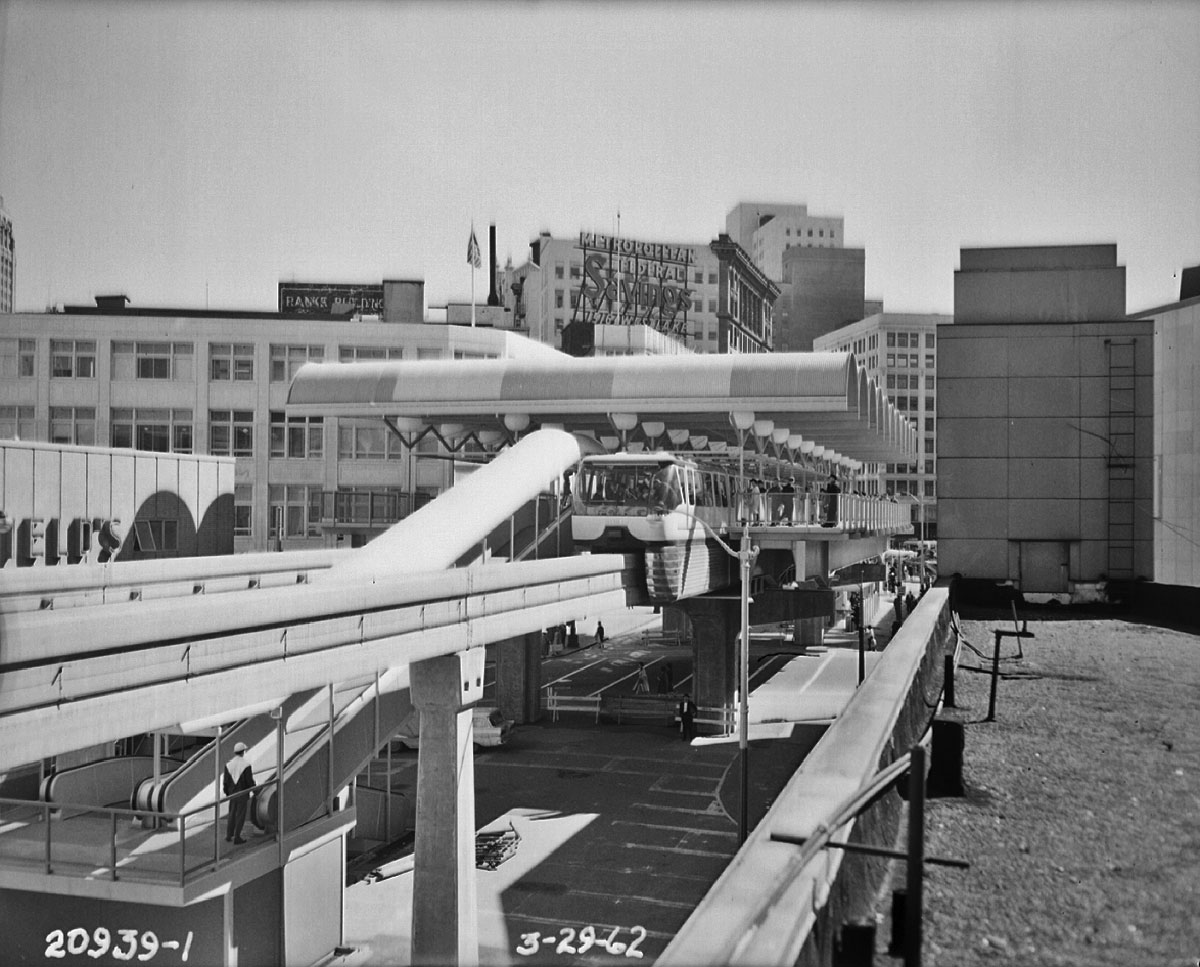
The Monorail Opens
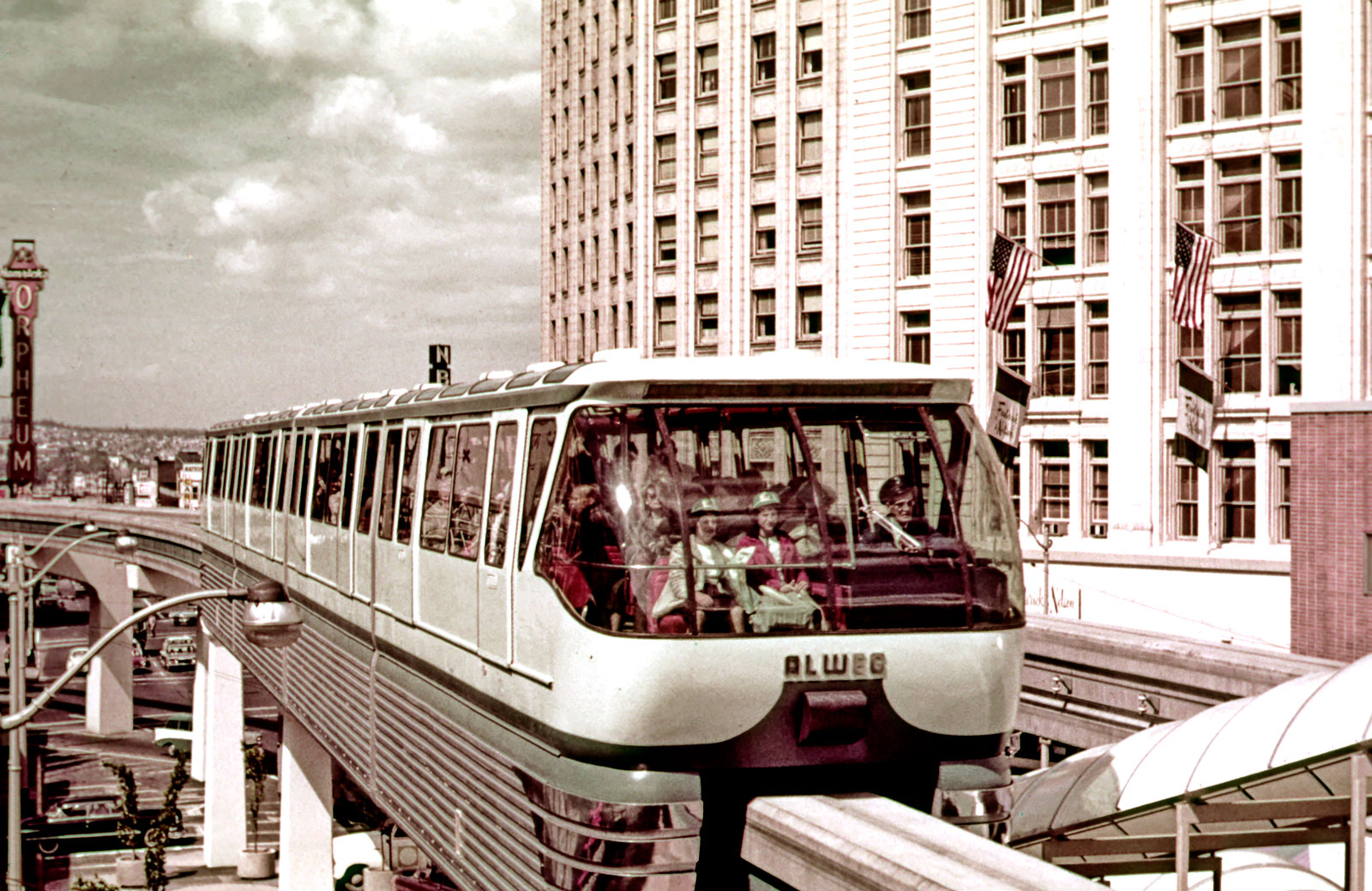
The Monorail opened to the public on March 24, 1962 nearly one month before the start of the World’s Fair. At a cost of $3.5 million, the trains carried more than eight million guests during the six months of the fair, easily paying for the cost of construction. The full initial capital cost of the system was recovered and a profit was realized by ALWEG before the end of the fair.

1962
1965
April 1965
The City gets the Monorail
Following the Fair, the Monorail system was turned over to Century 21 Corporation at no cost. Century 21 sold the system to the City of Seattle in 1965 for $600,000.
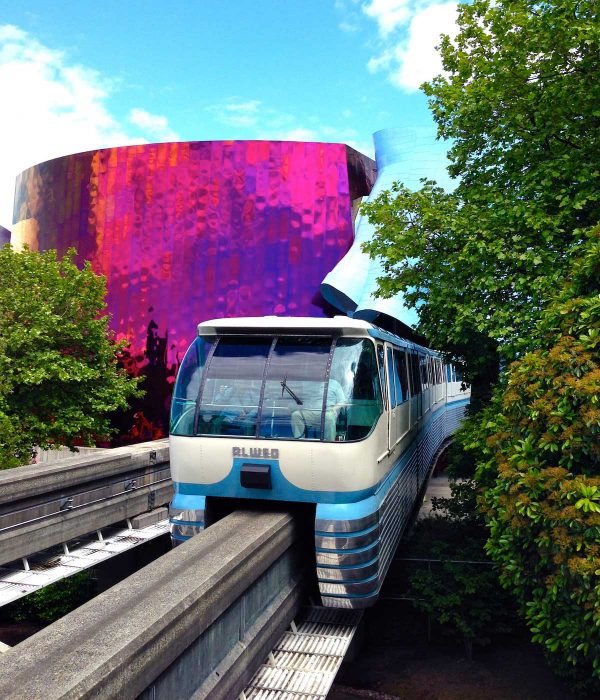



Learn more about this historic system
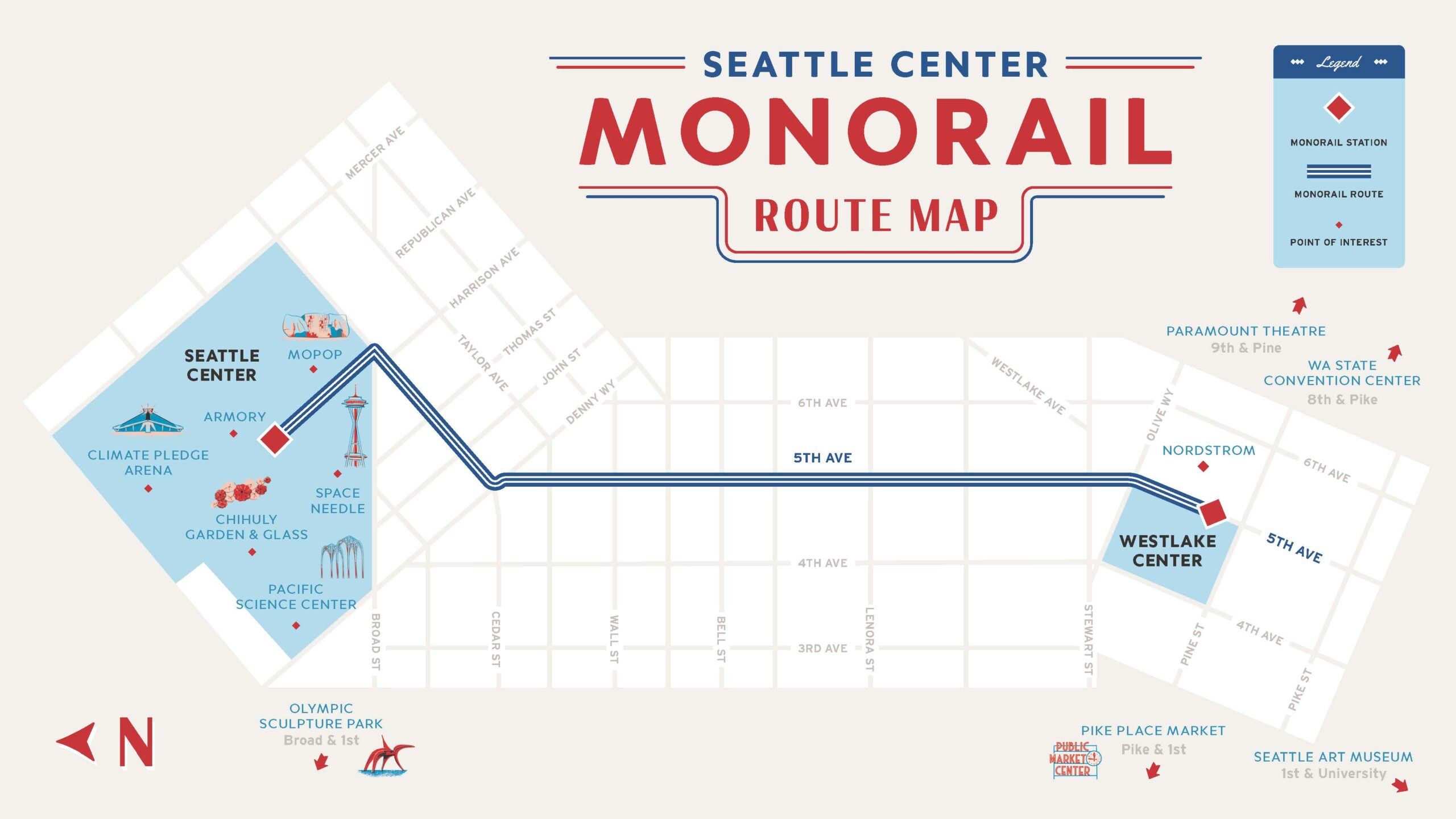
Seattle Center Monorail system is composed of two trains and a fixed guideway. Each train runs on its own dedicated “rail,” which is composed of 68 y-shaped columns supporting pairs of concrete beams, which span the columns. The typical pre-stressed concrete beams are approximately 70ft long. The highest columns are around 30ft overhead. The guideway is just under 1 mile in length at the present day, but when it was built in 1962, it extended beyond Westlake Center and was a little longer than 1 mile. Construction of the guideway began in April 1961 and was completed in January 1962.
There are two trains: Blue Train and Red Train. The trains were built by ALWEG Rapid Transit Company in West Germany in 1961, and were shipped to New York City where they were placed on traditional rail cars and transported to Seattle. Blue Train arrived before Red Train, and was placed on the beam in February 1962. On March 3, 1962, Blue Train made its first test run.
Each train has 64 tires: 16 load-carrying tires ride on top of the beam, and 48 guide tires run along the sides of the beam for alignment purposes. The 16 load tires run as duals in eight wheel/suspension assemblies called “bogies.” Each bogie has 2 load tires, 6 guide tires, an air suspension system, a 700VDC motor, gearbox and drive train, and a brake assembly. The motors were manufactured by GE and the gear boxes were built by Rockwell.
The Monorail trains run on 700 volts DC, which is supplied to the trains through contact rails on each beam. Carbon shoes contact the copper-headed rail to transfer power to the propulsion system, which in turn supplies current to the DC motors.
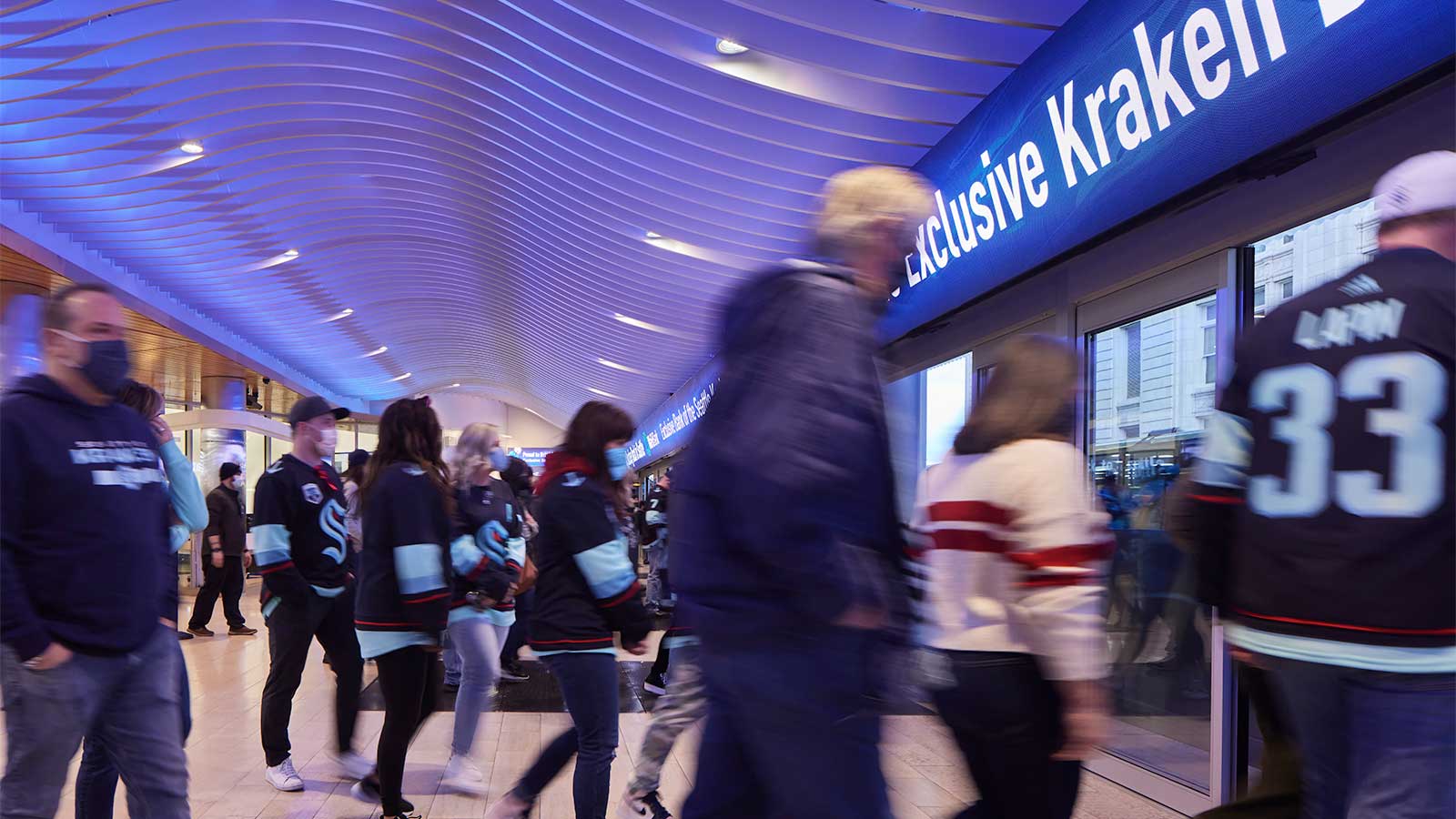
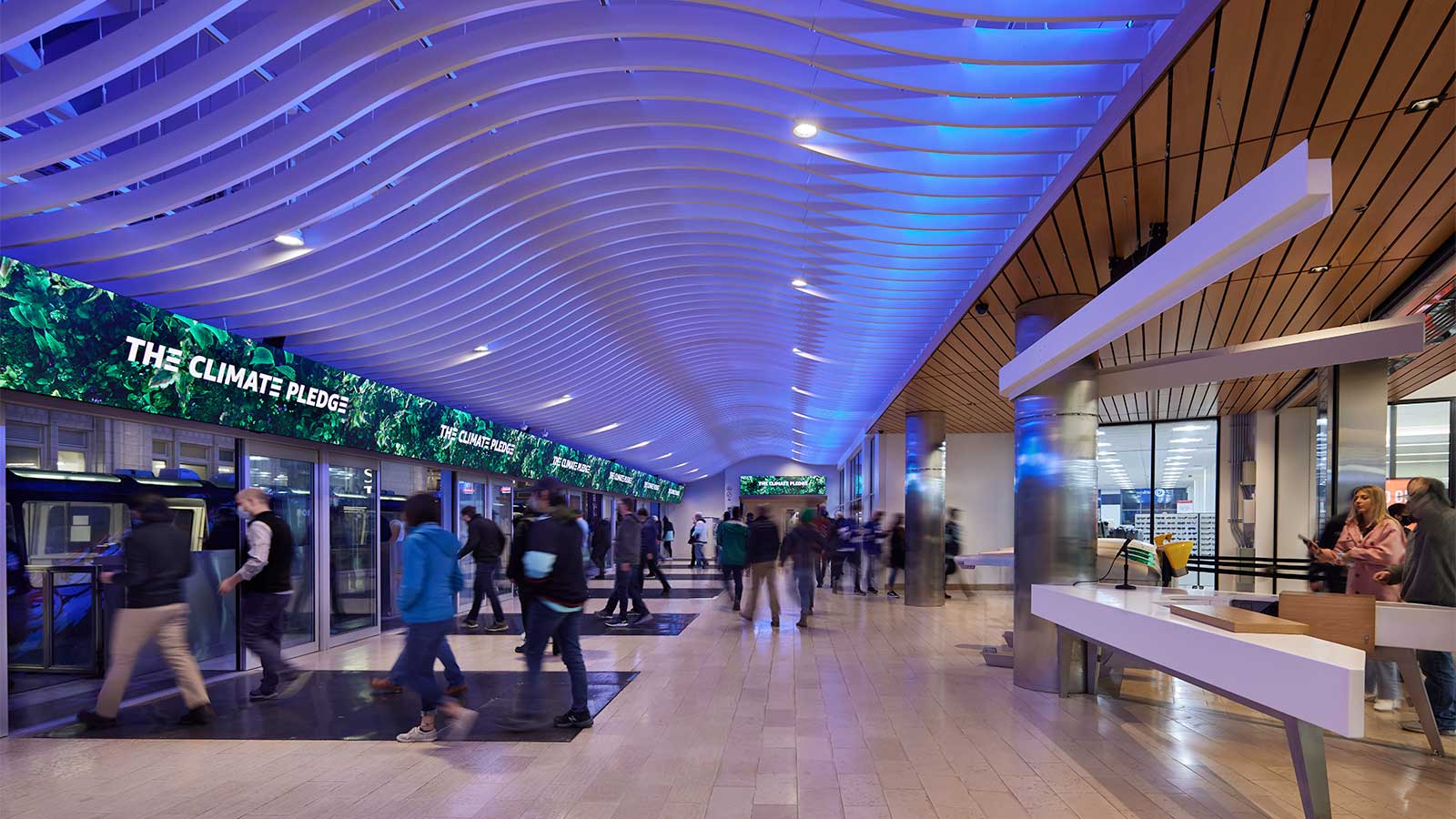
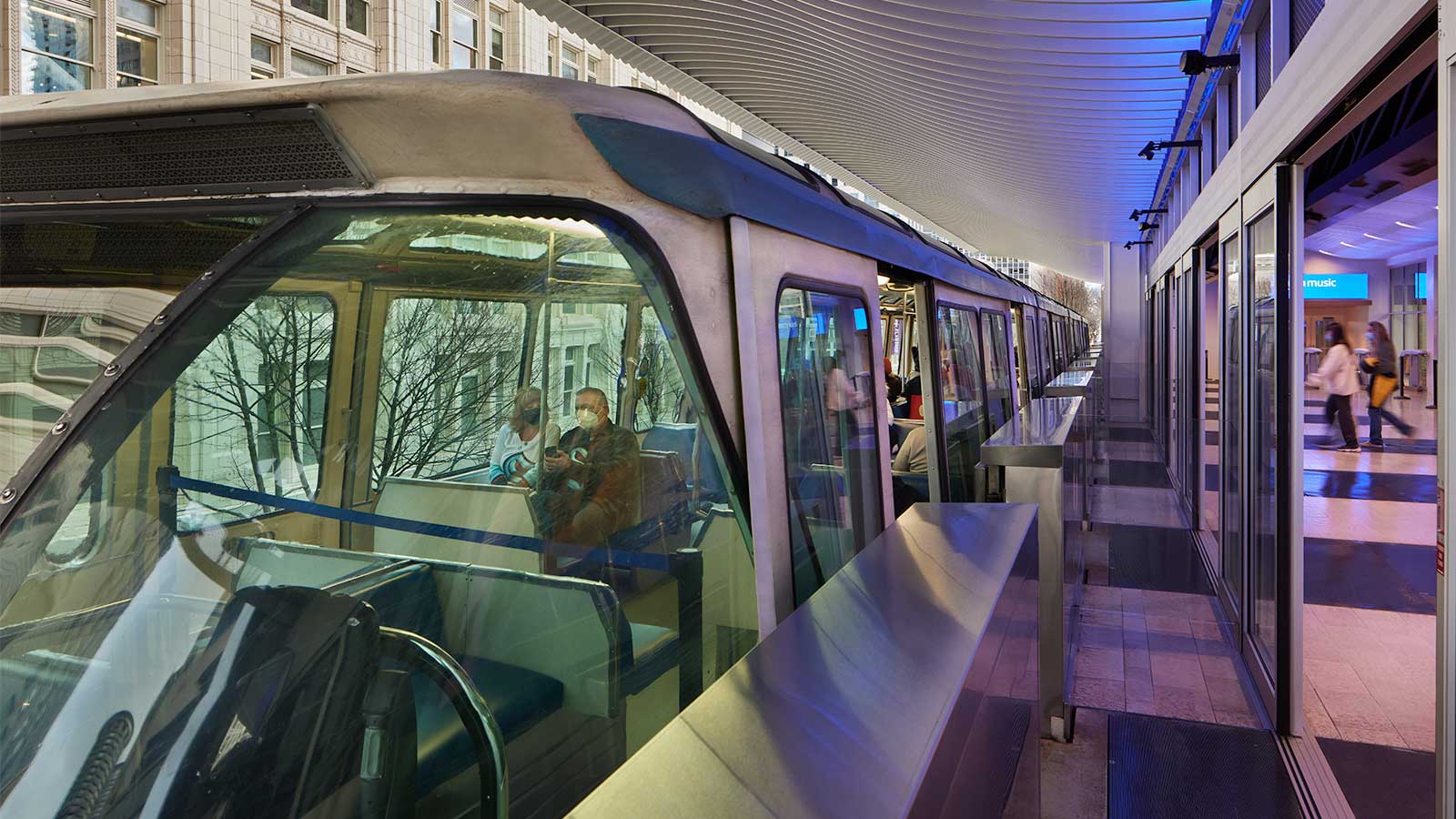



In 2021, Seattle Monorail Services completed $7M of privately funded improvements to Westlake Monorail Station. These station improvements were made as a result of the 2018 Seattle Center Monorail Stations Reconfiguration Evaluation Report completed by VIA Architecture. These improvements have increased the system’s capacity, improved accessibility, and better connect the monorail with the regional transit network, downtown transportation infrastructure, and other downtown resources.
A headline about passengers goes here.
Seattle Center Monorail carries over two million passengers each year. Our passengers are a combination of locals who use the system to travel to work, school, and events taking place at Seattle Center or downtown, as well as domestic and international tourists visiting Seattle.
Flying over the hustle and bustle of Seattle is the best part of my morning Monorail commute. When you emerge from the MoPop tunnel and all of the city is spread before you, I’m reminded of why I love living here

I never know how my workday will go, but I always know the monorail crew will help jump start my day and end my day leaving me happy and feeling good. The ride is ONLY two minutes, but some of my best friends were made from years of those two-minute interactions!